Imagine embarking on a self-sufficient adventure, living off the grid with your family. Your backyard transforms into a thriving survival garden, teeming with fresh produce. You learn to identify wild plants for sustenance, while cautiously avoiding any poisonous imposters. Disaster preparedness empowers you to care for your pets during emergencies, while DIY projects like building a homemade water filter and a solar power system ensure self-reliance. Even the younger explorers get involved, mastering basic survival skills like building shelters and making fire without matches. This exciting journey into off-grid living isn’t just about doomsday prepping, but rather about embracing self-reliance, connecting with nature, and equipping yourself and your loved ones with valuable skills. One crucial aspect of this journey is learning bleed control: essential first-aid techniques to stop bleeding fast. By acquiring these skills, you’ll gain the confidence and knowledge to handle unexpected situations with resilience and resourcefulness. So, are you ready to embark on your own off-grid adventure and learn how to deal with bleeding effectively?
Understanding the Basics of Bleeding
Different types of bleeding
Bleeding can occur in different ways, and it’s important to understand the various types of bleeding that can occur. The three main types are arterial bleeding, venous bleeding, and capillary bleeding.
Arterial bleeding is the most severe type of bleeding, as it involves blood being pumped directly from an artery. The blood is bright red and often spurts out in a rhythmic pattern. Venous bleeding, on the other hand, occurs when blood is flowing from a vein. It is typically a steady flow and the blood is dark red. Capillary bleeding is the least severe type and is characterized by a slow, oozing flow of blood from damaged capillaries. This type of bleeding is usually more superficial and can be easier to control.
Causes of bleeding
Bleeding can be caused by a variety of factors. It can result from an injury, such as a cut or a puncture wound, or from a medical condition, such as a nosebleed or internal bleeding. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can also increase the risk of bleeding. It’s important to understand the cause of the bleeding in order to determine the best course of action for stopping it.
Signs and symptoms of severe bleeding
Severe bleeding can have noticeable signs and symptoms that indicate the need for immediate attention. These may include heavy or rapid blood loss, blood pooling around the wound, difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, pale or cold skin, and signs of shock, such as confusion or loss of consciousness. It’s crucial to recognize these signs and take prompt action to control the bleeding and seek medical help.
Assessing the Severity of the Bleeding
Determining the amount of blood loss
Assessing the amount of blood loss is an essential step in determining the severity of the bleeding. Keep in mind that just because there is a large amount of blood present does not necessarily mean that it is life-threatening. It is important to consider the rate of blood loss and the body’s ability to compensate for it.
Identifying mild, moderate, and severe bleeding
Once the amount of blood loss has been determined, it’s important to identify whether the bleeding is mild, moderate, or severe. Mild bleeding typically involves a slow, steady flow of blood that can be easily controlled. Moderate bleeding may have a faster flow of blood that is more difficult to control. Severe bleeding is characterized by a rapid, uncontrolled flow of blood that poses a serious risk to the individual’s life.
Recognizing life-threatening bleeding
Life-threatening bleeding is a medical emergency that requires immediate action. It is typically characterized by massive blood loss, an inability to control the bleeding, and signs of shock. If you encounter someone with life-threatening bleeding, it is important to act quickly to control the bleeding and seek immediate medical help.

Immediate Actions for Bleed Control
Maintaining personal safety
Before attempting to control bleeding, it’s crucial to ensure your own safety. Put on personal protective equipment, such as gloves, to protect yourself from exposure to bloodborne pathogens. If necessary, move the injured person to a safe location away from any potential dangers, such as traffic or hazardous materials.
Calling for emergency medical help
While taking immediate actions to control bleeding is important, it is equally important to call for emergency medical help. This ensures that professional medical assistance is on the way and can provide additional support and treatment. Be prepared to provide accurate information about the location, nature of the injury, and the severity of the bleeding when contacting emergency services.
Applying direct pressure to the wound
One of the most effective methods for controlling bleeding is applying direct pressure to the wound. Use a clean cloth, gauze, or your hand to apply firm and continuous pressure directly on the bleeding site. Maintain the pressure until the bleeding stops or medical professionals take over. If blood soaks through the first layer of cloth or gauze, do not remove it. Instead, add another layer on top and continue applying pressure.
Using Pressure Dressings and Bandages
Different types of dressings and bandages
When direct pressure alone is not enough to control bleeding, the use of pressure dressings and bandages can be helpful. Pressure dressings, such as sterile gauze pads or trauma pads, provide additional pressure and absorb blood. Elastic bandages, such as self-adherent wraps or stretchy gauze, can be used to secure the dressing and maintain pressure.
Applying pressure dressings
To apply a pressure dressing, place a sterile gauze pad or trauma pad directly on the wound. Apply firm pressure with your hand to maintain control over the bleeding. Once bleeding is under control, secure the dressing with an elastic bandage, wrapping it firmly but not too tight. Ensure that the pressure is evenly distributed over the wound.
Securing bandages properly
Properly securing bandages is crucial to maintaining pressure and preventing them from slipping or becoming loose. Start by wrapping the bandage around the dressing, making sure to cover all edges. Continue to wrap the bandage firmly, but not too tight, ensuring that it is snug enough to stay in place. Secure the end of the bandage with tape or a clip to prevent unraveling.

Utilizing Tourniquets in Extreme Cases
When and how to use a tourniquet
Tourniquets are a last resort measure used in extreme cases when bleeding cannot be controlled by other means. They should only be used when there is a risk of death from uncontrolled bleeding and when professional medical help is not immediately available. To apply a tourniquet, place it high and tight on the limb, between the bleeding site and the heart. Secure the tourniquet and tighten it until the bleeding stops.
Proper placement and tightening
When applying a tourniquet, it’s important to place it proximal to the bleeding site, as close to the body as possible. Avoid placing it over a joint or directly over a fracture. Once the tourniquet is in place, tighten it until the bleeding stops. Make sure it is tight enough to completely stop the flow of blood, but not so tight that it causes excessive pain or damage to the limb.
Monitoring and releasing the tourniquet
Once a tourniquet has been applied, it’s important to continuously monitor the injured person’s condition. Watch for signs of the tourniquet being too tight, such as severe pain, numbness, tingling, or loss of pulse or sensation in the limb. If the tourniquet needs to be released, do so only in a controlled medical environment where immediate measures can be taken to control the bleeding.
Elevating the Wound to Reduce Bleeding
Understanding the concept of elevation
Elevating the wound can help reduce bleeding by taking advantage of the body’s natural mechanism to decrease blood flow to an injured area. When a wound is elevated above the level of the heart, gravity helps to reduce the pressure in the blood vessels, thus reducing bleeding.
Steps to safely elevate a wound
To safely elevate a wound, start by ensuring the injured person is in a comfortable position. Raise the wounded area above the level of the heart, using pillows or cushions if necessary. Make sure that the elevation does not put any strain or pressure on the injured area. It’s important to note that elevation alone is not sufficient to control severe bleeding, but it can be a useful additional measure.
Benefits and limitations of elevation
Elevation can be particularly helpful for minor bleeding or when waiting for medical help to arrive. It can help slow down the bleeding and provide some relief while other measures are being taken. However, it is important to note that elevation alone is not a substitute for direct pressure or other bleeding control techniques. In cases of severe bleeding, elevation should be combined with other interventions to effectively control bleeding.
Applying Hemostatic Agents
Overview of hemostatic agents
Hemostatic agents are substances that promote clotting and help control bleeding. They can be used in addition to direct pressure or when direct pressure alone is not sufficient. There are various types of hemostatic agents available, including powders, gauze, and sponges, which contain clotting agents such as kaolin or chitosan.
Types of hemostatic agents
Hemostatic agents come in different forms, including granules, powders, dressings, and gauze. Granules and powders can be poured directly onto the bleeding site, while dressings and gauze can be applied and secured to control bleeding. Some hemostatic agents also have antimicrobial properties, which can help prevent infection.
Proper application and precautions
When applying a hemostatic agent, follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Ensure that the bleeding site is adequately exposed and clean before applying the agent. Apply the agent directly to the bleeding site, making sure to cover all areas with direct pressure. Be cautious of any potential allergic reactions or contraindications, and seek professional medical help if needed.
Recognizing and Handling Internal Bleeding
Signs and symptoms of internal bleeding
Internal bleeding can be deceiving, as it may not always be visible on the outside. However, there are certain signs and symptoms that can indicate the presence of internal bleeding. These can include abdominal pain or swelling, bruising or discoloration, dizziness or fainting, and signs of shock. It’s important to be aware of these signs and seek immediate medical attention if they are present.
First-aid measures for internal bleeding
While first aid measures cannot directly address internal bleeding, they can help stabilize the injured person and improve their chances of survival. Encourage the injured person to rest in a comfortable position, preferably on their side with their knees bent. Keep them warm and monitor their vital signs, such as pulse and breathing rate. If they become unconscious or their condition worsens, call for emergency medical help immediately.
When to seek immediate medical attention
Internal bleeding can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. If you suspect someone has internal bleeding, it’s important to seek professional medical help right away. Do not attempt to treat it on your own, as internal bleeding often requires surgical intervention and other advanced medical techniques to stop the bleeding and prevent further complications.
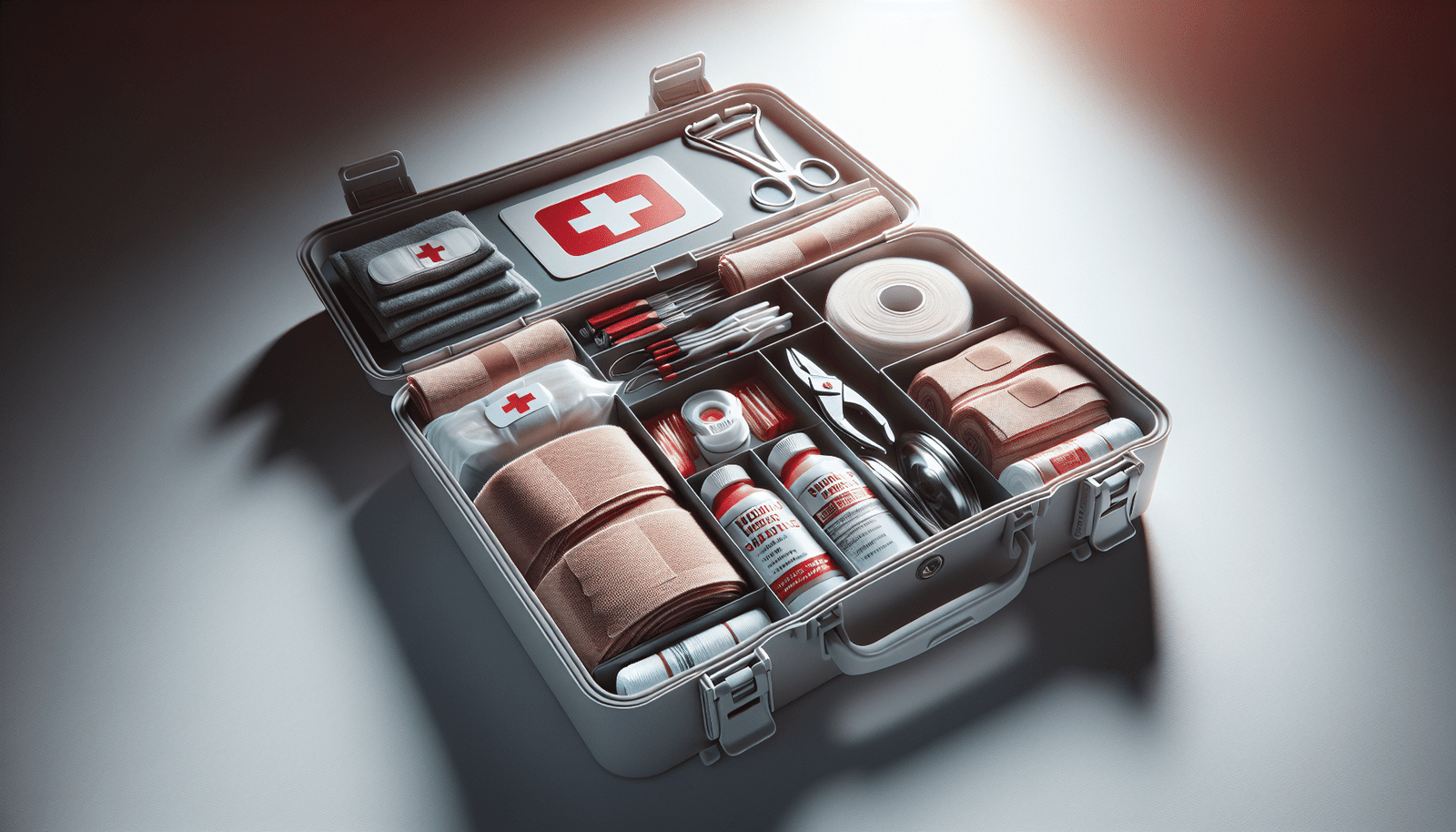
Maintaining a First-Aid Kit for Bleed Control
Essential items to include in a first-aid kit
A well-stocked first-aid kit is essential for managing bleeding emergencies effectively. Some essential items to include in a bleed control kit are sterile gauze pads, adhesive bandages of various sizes, adhesive tape, elastic bandages, emergency pressure dressings, a tourniquet, hemostatic agents, gloves, and scissors. It’s also important to periodically check expiration dates and replace any items that have been used or are no longer in good condition.
Proper organization and storage
Proper organization and storage of your first-aid kit ensure that you can quickly locate items when needed. Designate specific compartments or pouches for different categories of items, such as dressings, bandages, and hemostatic agents. Consider using clear, sealable bags for smaller items to keep them organized and easily visible. Store the first-aid kit in a location that is easily accessible and known to all members of the household.
Regular inspection and restocking
Regularly inspecting and restocking your first-aid kit is essential to ensure that it is ready for use when needed. Check expiration dates on medications and sterile items and replace any expired items. Restock any items that have been used, such as bandages or dressings, and replenish your supply of gloves or other disposable items. It’s better to be prepared and have a fully stocked first-aid kit for any bleeding emergencies that may arise.
Seeking Professional Medical Help
Knowing the limitations of first-aid
While knowing first-aid techniques for bleeding control is crucial, it’s important to recognize the limitations of first-aid and when professional medical help is needed. First-aid measures can help stabilize a person’s condition and control bleeding temporarily, but they cannot replace specialized medical treatment. Professional medical help is necessary to assess and treat the underlying cause of bleeding and provide more advanced interventions if needed.
When to transfer care to medical professionals
It’s important to transfer care to medical professionals in certain situations, even if bleeding is under control. These situations include severe or life-threatening bleeding, suspected internal bleeding, bleeding that does not stop despite initial first-aid measures, injuries involving major arteries or organs, or any other circumstances where specialized medical treatment is required. Do not hesitate to call for emergency medical help and follow the instructions given by healthcare professionals.
Providing accurate information to healthcare providers
When seeking professional medical help for bleeding, it’s important to provide accurate and detailed information to healthcare providers. This includes describing the mechanism of injury, the location and severity of bleeding, any first-aid measures that have been taken, and the injured person’s current condition. The more information you can provide, the better healthcare professionals will be able to assess the situation and provide appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, having a thorough understanding of bleed control techniques is essential for anyone who may be in a position to assist in an emergency involving bleeding. From identifying different types of bleeding to applying direct pressure and utilizing hemostatic agents, the knowledge and skills outlined in this article can help save lives. Remember to prioritize personal safety, always call for professional medical help, and seek further training and certification in first-aid techniques to confidently handle bleeding emergencies. With these techniques in your toolkit, you can become a reliable responder in times of need and make a positive impact in your community.